Anaplasmosis: What You Need to Know
When dealing with anaplasmosis, a bacterial infection transmitted by tick bites that triggers fever, muscle aches, and sometimes severe complications. Also known as tick fever, it’s caused by a specific bacterium and can be confused with other tick‑borne illnesses.
Key Related Factors
Understanding Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the microscopic pathogen that invades white blood cells is essential because it defines the disease’s biology. The primary vector is the tick, especially the black‑legged (Ixodes) species that also spreads Lyme disease. Early identification matters: doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic is the go‑to treatment and works best when started within a few days of symptom onset. Prevention hinges on tick prevention, practices like wearing repellents, checking skin after outdoor activities, and managing vegetation. These steps lower the chance of picking up not only anaplasmosis but also other tick‑borne diseases such as Lyme disease, which often co‑occurs.
In practice, anaplasmosis follows a clear chain: the tick bites a host, transfers Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the bacteria multiply inside neutrophils, and the immune response generates fever, chills, and headache. Diagnosis usually relies on blood tests that detect the organism’s DNA or antibodies. Because symptoms overlap with other infections, clinicians compare lab results with exposure history—did you spend time in grassy or wooded areas?—to pinpoint the cause. Once confirmed, a short course of doxycycline typically resolves the infection, but delayed treatment can lead to respiratory failure or organ damage, especially in older adults or immunocompromised patients.
Preventive measures form the final piece of the puzzle. Regularly inspect clothing and skin after hikes, use EPA‑registered repellents containing DEET or picaridin, and keep lawns trimmed to reduce tick habitats. Pets should also be treated, as they can bring ticks indoors. By breaking the tick‑to‑human transmission cycle, you dramatically cut the risk of anaplasmosis and related co‑infections.
Below you’ll find a curated selection of articles that dive deeper into each of these aspects—diagnostic methods, treatment protocols, co‑infection risks, and practical prevention tips. Whether you’re a patient, a caregiver, or a health professional, the resources listed will give you actionable insight and up‑to‑date guidance on managing anaplasmosis.
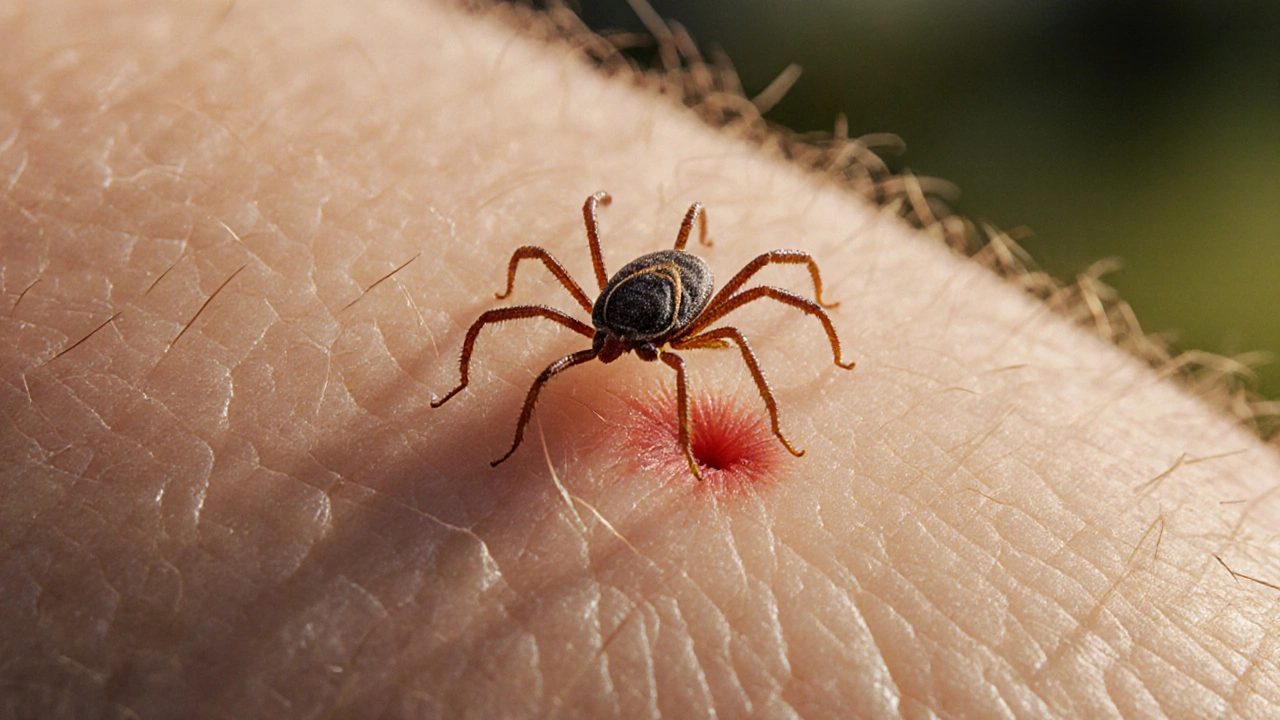

Tick Fever and the Immune System: How the Disease Affects Your Body’s Defenses
Discover how tick fever (anaplasmosis) disrupts the immune system, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tips to keep your defenses strong.