If you’ve been told you have intermediate age-related macular degeneration (AMD), you might have been handed a bottle of pills labeled AREDS2 vitamins and told to take them daily. But what exactly are these vitamins? Do they work? And are they right for you? The answers aren’t as simple as popping a pill - they’re rooted in over two decades of rigorous science.
What Are AREDS2 Vitamins?
The AREDS2 formula isn’t just another multivitamin. It’s a specific, clinically tested blend of nutrients designed to slow the progression of a serious eye disease called age-related macular degeneration. This isn’t a guess or a trend - it’s the result of a 12-year, $85 million clinical trial run by the National Eye Institute (NEI), one of the largest and most respected eye research programs in the world.
The original AREDS formula, released in 2001, showed that a mix of vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, copper, and beta carotene could reduce the risk of advanced AMD by about 25%. But researchers noticed a problem: beta carotene raised the risk of lung cancer in people who smoked or used to smoke. That’s where AREDS2 came in.
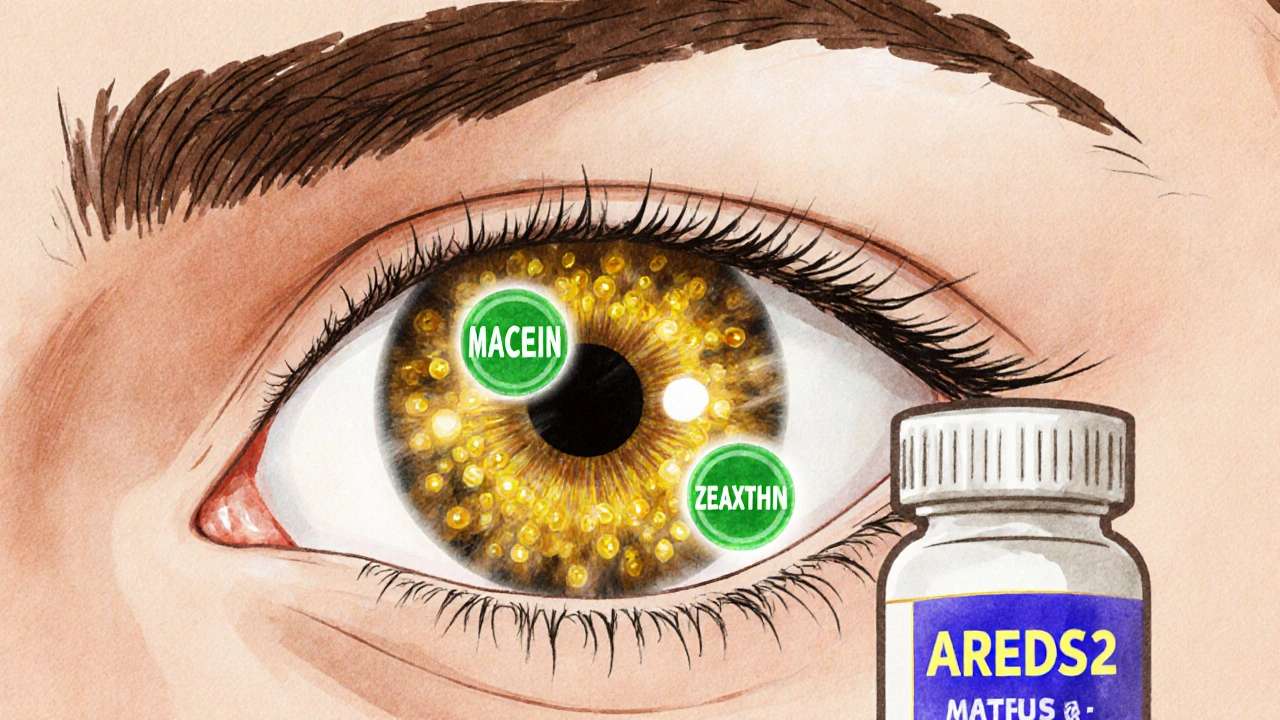
The updated formula, finalized in 2013, replaced beta carotene with two powerful carotenoids: lutein (10 mg) and zeaxanthin (2 mg). These are natural pigments found in green leafy vegetables, corn, and egg yolks. They’re the only nutrients in the macula - the part of the eye responsible for sharp central vision - that act like internal sunglasses, filtering out harmful blue light.
The final AREDS2 formula includes:
- 500 mg of vitamin C
- 400 IU of vitamin E
- 80 mg of zinc (as zinc oxide)
- 2 mg of copper (as cupric oxide)
- 10 mg of lutein
- 2 mg of zeaxanthin
This isn’t a suggestion - it’s the exact dosage proven in clinical trials. Taking less, more, or swapping ingredients won’t give you the same benefit. And yes, the copper is there for a reason: high zinc levels can lower copper in your body, so it’s added to prevent deficiency.
Who Should Take AREDS2 Vitamins?
This is where most people get it wrong. AREDS2 vitamins are not for everyone. They’re not a preventive tool. They’re not for people with early AMD or no AMD at all.
The only people who benefit are those with intermediate AMD in one or both eyes - that means lots of medium-sized drusen (yellow deposits under the retina) or at least one large drusen. Or, if you have advanced AMD in one eye (like geographic atrophy) and intermediate AMD in the other.
If you have only small drusen - the kind often seen in early AMD - taking these supplements won’t help. A 2023 analysis from Vision-and-Eye-Health.com put it bluntly: “The AREDS2 formula does not offer benefits for individuals with early AMD, nor does it prevent the onset of the condition.”
And here’s the hard truth: these vitamins cannot reverse vision loss that’s already happened. They don’t restore sight. They don’t cure AMD. They simply slow the clock. For someone with intermediate AMD, taking the formula reduces the chance of moving to late-stage AMD - where central vision is lost - by about 26% over 10 years, according to a 2022 JAMA Ophthalmology study tracking nearly 4,000 people.
Why Lutein and Zeaxanthin Beat Beta Carotene
The switch from beta carotene to lutein and zeaxanthin wasn’t just about safety - it was about better results.
In the original AREDS trial, beta carotene was linked to a 20% higher risk of lung cancer in current and former smokers. That’s not a small risk. For someone who smoked for decades, that could mean the difference between life and death.
AREDS2 showed that lutein and zeaxanthin didn’t carry that risk. In fact, they worked better. The 10-year follow-up confirmed a 26% reduction in progression to late AMD with lutein/zeaxanthin, compared to 25% with the old beta carotene formula. For people with low dietary intake of these nutrients - meaning they don’t eat spinach, kale, or corn regularly - the benefit was even stronger.
And here’s something surprising: omega-3 fatty acids, which many people thought would help, added nothing. The study tested adding DHA and EPA - the omega-3s found in fish oil - and found no extra protection. That ruled out a popular assumption and helped streamline the formula.
New Findings: AREDS2 Might Help Late-Stage AMD Too
In July 2024, researchers made a breakthrough that changed how we think about these supplements.
For years, AREDS2 was only recommended for intermediate AMD. But a new analysis of 1,209 participants from the original trial showed something unexpected: the formula also slowed the progression of geographic atrophy - the advanced, late-stage form of dry AMD - by 55% over three years, when the damage was outside the central fovea.
That’s huge. Geographic atrophy used to be seen as untreatable. Now, for people whose vision loss hasn’t yet reached the very center of the macula, AREDS2 might help them hold onto functional vision longer. Geraldine Hoad of the Macular Society called the results “encouraging,” noting that slowing vision loss could help people stay independent longer.
But there’s a caveat: this finding comes from a post-hoc analysis of existing data, not a new trial. More research is needed to confirm it. Still, it’s the most promising development in AMD treatment in years.
What About Prevention? Can You Take AREDS2 to Avoid AMD?
No. And this is critical.
Many people buy AREDS2 supplements hoping to prevent AMD before it starts. That’s a waste of money - and possibly a waste of your health.
Studies have shown no benefit for people with early AMD or no AMD at all. Dr. Emily Chew, who led the AREDS2 research, says clearly: “AREDS supplements cannot reverse vision damage that has already occurred, and they have no preventative effect for those with early AMD.”
Trying to use them early won’t stop you from getting AMD. It won’t make your eyes stronger. It won’t protect you from blue light or screen time. Those are myths.
If you’re under 60 and have perfect vision, skip the pills. Focus on eating leafy greens, not taking supplements. If you’re over 60 and have been diagnosed with intermediate AMD - then talk to your eye doctor about starting AREDS2.

How to Take Them and What to Watch For
Take the supplements daily, exactly as labeled. Missing doses reduces their effectiveness. They’re not fast-acting - you need to take them for years to see results.
Some people experience mild side effects: stomach upset from the high zinc dose, or a slight metallic taste. These usually fade. But if you have kidney disease or are on certain medications, talk to your doctor first. High zinc can interfere with copper and iron absorption.
Also, don’t combine AREDS2 with other multivitamins unless you’re sure you’re not doubling up on zinc or vitamin E. Too much zinc over time can cause nerve damage. Too much vitamin E might increase bleeding risk.
Always buy from reputable brands. Look for third-party testing (like USP or NSF) on the label. Many store brands cut corners - they might not contain the right amounts or might use cheaper forms of the nutrients.
What’s Not Included - and Why
You’ll notice the AREDS2 formula doesn’t have:
- Omega-3s
- Anthocyanins (from blueberries)
- Coenzyme Q10
- Astaxanthin
That’s because none of these were proven to help in the AREDS2 trial. Just because a supplement claims to support “eye health” doesn’t mean it works for AMD. The only proven combo is the one above.
Be wary of products that call themselves “AREDS2-style” or “doctor-recommended.” If the label doesn’t list the exact dosages I mentioned, it’s not the real thing.
Final Takeaway: It’s Not About Taking Pills - It’s About Timing
AREDS2 vitamins are one of the few treatments in eye care with solid, long-term evidence. But they’re not magic. They’re a targeted tool for a specific stage of a specific disease.
If you have intermediate AMD - get tested, get the right formula, and take it daily. If you don’t - don’t waste your money. Eat your greens. Get regular eye exams. Protect your eyes from UV light.
The science is clear: these supplements work - but only for the right people, at the right time. And that’s the difference between hope and real, lasting results.
Are AREDS2 vitamins safe to take long-term?
Yes. A 10-year follow-up study of nearly 4,000 participants found no major safety concerns with the AREDS2 formula. The combination of vitamins and minerals was well-tolerated over a decade, with no increase in serious side effects compared to placebo. Long-term use is considered safe under medical supervision.
Can I get the same benefits from food instead of pills?
While lutein and zeaxanthin are found in spinach, kale, corn, and eggs, you’d need to eat several cups daily to match the 10 mg and 2 mg doses in AREDS2. Most people can’t achieve this through diet alone. The supplement delivers a concentrated, consistent dose that’s proven to work in clinical trials.
Should I take AREDS2 if I’m a smoker?
Yes - but only if you have intermediate or advanced AMD. Unlike the original AREDS formula, AREDS2 does not contain beta carotene, which was linked to lung cancer in smokers. Lutein and zeaxanthin are safe for current and former smokers, making this the only recommended vitamin formula for them.
Do AREDS2 vitamins help with wet AMD?
No. AREDS2 supplements are designed for dry AMD - the slow-progressing form characterized by drusen and geographic atrophy. Wet AMD involves abnormal blood vessel growth and is treated with injections or laser therapy. The vitamins do not affect wet AMD.
What if I have AMD in only one eye?
You should still take AREDS2 if you have intermediate AMD in one eye and advanced AMD in the other. Studies show the supplements reduce the risk of progression in the healthier eye. Even if only one eye is affected now, the goal is to protect the other from advancing.





Ryan Anderson
November 14, 2025 AT 12:11Just want to say this is one of the clearest breakdowns of AREDS2 I’ve ever read. No fluff, no hype - just the science. I’ve been taking these for 4 years since my intermediate AMD diagnosis, and my optometrist says my drusen count hasn’t changed. That’s huge.
Also, third-party tested brands only. I use Nature Made USP Verified. Don’t risk some random Amazon brand that says ‘AREDS2-style’ but has half the zinc.
gent wood
November 15, 2025 AT 04:14Thank you for writing this. So many people assume supplements are a cure-all - but this is precision medicine for the eyes. The fact that lutein and zeaxanthin replaced beta carotene without losing efficacy - and actually improved safety - is a triumph of clinical research.
I’m a 68-year-old former smoker. I used to take the original AREDS. Now I take AREDS2. No lung cancer scare. No regrets.
Ashley Durance
November 15, 2025 AT 23:11Let’s be real - most people buying these don’t even know what intermediate AMD looks like. They see ‘eye vitamins’ on a shelf, think ‘I’m getting old, better be safe,’ and buy it. Then they wonder why their vision didn’t improve.
The 2023 analysis you cited? That’s the nail in the coffin for prevention myths. If you have early AMD or no AMD, you’re just spending $30/month on placebo with side effects.
And don’t even get me started on blueberry supplements. Anthocyanins? Cute. Not proven. Not relevant. Stop marketing pseudoscience as ‘eye health.’
Also - copper is non-negotiable. I’ve seen people take zinc-only pills and end up with anemia. That’s not ‘natural.’ That’s dangerous.
And omega-3s? The trial was massive. 4,000 people. 10 years. No benefit. End of story. Stop adding fish oil to everything just because it sounds healthy.
People need to stop treating supplements like vitamins for the soul. This isn’t yoga. It’s pharmacology with a label.
And if you’re under 60 and not diagnosed? Eat spinach. Not pills.
And if you’re over 60 and still smoking? Good for you for switching to AREDS2. But quit smoking. The vitamins don’t undo that damage.
And if you think this helps wet AMD? No. Just no. Injections are the treatment. Don’t confuse the two.
This isn’t a supplement. It’s a medical protocol. Treat it like one.
Kevin Wagner
November 17, 2025 AT 00:48Bro. I was skeptical too. Thought it was just another scam. But after my doc showed me my OCT scan - all those little yellow drusen dots? - and said ‘this is intermediate,’ I started AREDS2. Two years later? No progression. No new blind spots. No scary ‘late-stage’ talk.
I eat kale. I walk. I wear sunglasses. But this? This is the only thing that’s actually working. I’m not some super-healthy guy. I’m just a guy who followed the science. And it’s paying off.
Don’t let the internet noise fool you. This isn’t magic. It’s math. And the math works.
Eleanora Keene
November 17, 2025 AT 18:52Thank you for sharing this. I’m a nurse and I’ve seen so many patients waste money on ‘eye health’ supplements that have zero evidence. This is the kind of clarity we need.
I always tell my patients: If it doesn’t list the exact dosages from the AREDS2 trial, it’s not the real thing. And if it says ‘supports vision’ without mentioning AMD? Run.
You’re doing important work here. Keep it up.
Barry Sanders
November 19, 2025 AT 02:58Wow. Another ‘science’ article that ignores the truth. The real reason AREDS2 works? Placebo effect. And the ‘10-year study’? Funded by the NIH - which is basically Big Pharma’s cousin.
Meanwhile, real nutrients like astaxanthin and CoQ10? Silenced. Suppressed. Because they can’t be patented.
Wake up. This isn’t medicine. It’s corporate control disguised as science.
Dilip Patel
November 20, 2025 AT 00:28USA always think they have all answers. In India we use turmeric and amla for eyes. Much better than pills. Why you waste money on zinc? Our grandmas know better.
Also why you not say about Ayurveda? All this science is just for sell pills. I think this is fake.
Peter Aultman
November 20, 2025 AT 09:05Just took AREDS2 for 3 years. No side effects. My drusen stayed the same. My doc says that’s a win.
Don’t overthink it. If you’ve been told you have intermediate AMD - take the pills. If not - don’t. Eat your greens. Done.
Scott Saleska
November 21, 2025 AT 22:52Wait - so if you have AMD in one eye and it’s intermediate, you should take it even if the other eye is fine? That’s what the article says? But isn’t that like taking antibiotics for a cold just because you had pneumonia last year?
I get the logic - protecting the other eye - but it feels like over-treatment. What if you’re just one of the 74% who won’t progress? Are you really going to take pills for 10+ years just in case?
I’m not saying no - I’m saying I’d want more data on individual risk before committing.
Sean Hwang
November 23, 2025 AT 07:27My dad took these after his diagnosis. He’s 78. Still drives. Still reads. Doesn’t have the big blind spot in the middle like his buddy down the street who skipped the pills.
He doesn’t even remember the names of the vitamins. Just takes ‘the eye pills’ every morning with his coffee.
That’s all you need to know.
Jane Johnson
November 24, 2025 AT 03:23Interesting. But where is the data on long-term zinc toxicity? You mention it briefly. But the FDA warns of neurological damage at doses above 40mg daily. This formula has 80mg. That’s double the upper limit.
And yet you call it ‘safe.’
Contradiction.
Chris Ashley
November 24, 2025 AT 19:56So if I’m 55 and have small drusen, I shouldn’t take them? Even though I’m scared I’ll get AMD? I mean, what’s the harm?
Joe Goodrow
November 26, 2025 AT 02:53USA science is great. But you’re ignoring the real solution: get out of the city. Fresh air. Less screens. More sun. No pills needed. We used to live like this. Now you’re all addicted to chemicals.
My cousin in Texas - he’s 70, never took a vitamin. Still sees fine. He mows his lawn every day. That’s your cure.